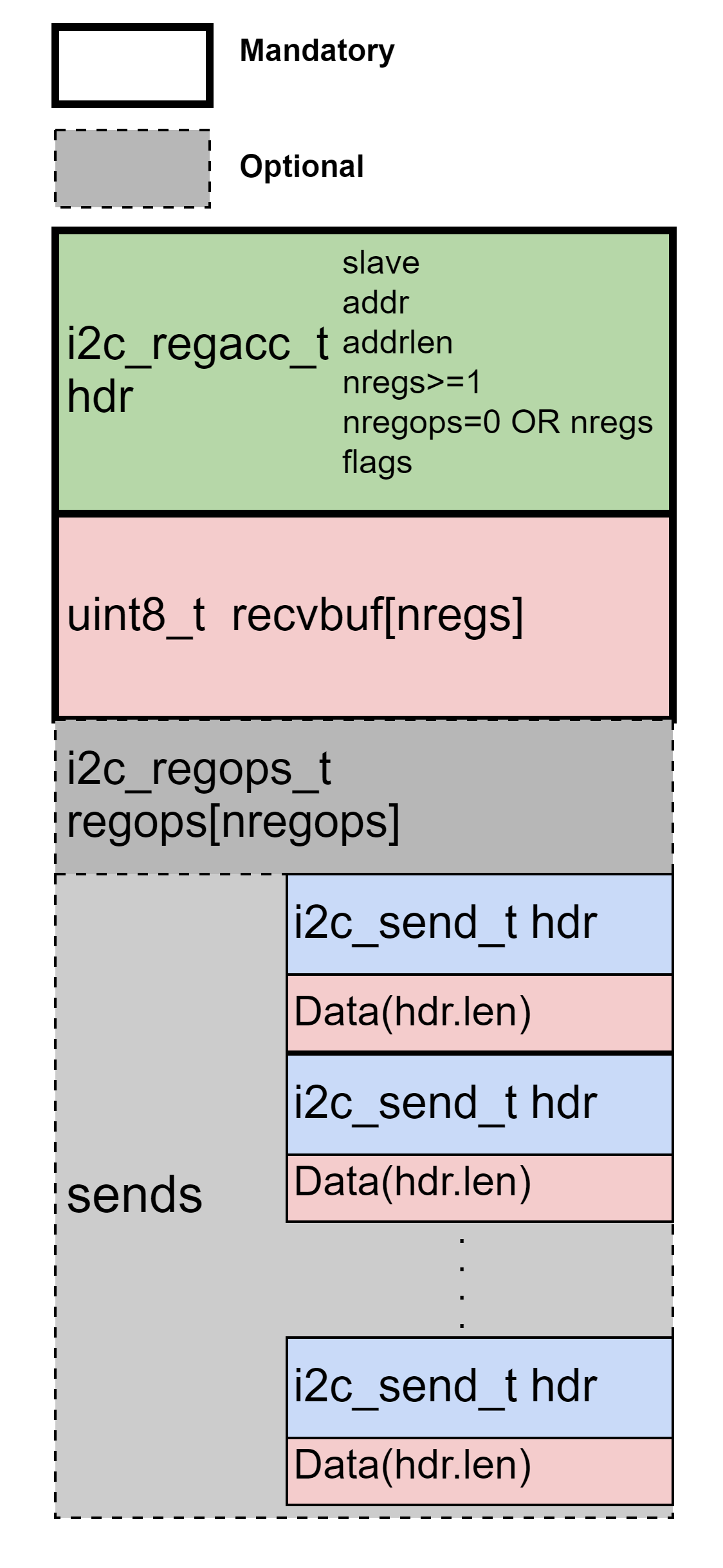
DCMD_I2C_REGACC
QNX SDP8.0Customizing a BSPConfigurationDeveloper
#include <hw/i2c.h>
#define DCMD_I2C_REGACC __DIOTF(_DCMD_I2C, 12, i2c_regacc_t)
The arguments to devctl() are:
| Argument | Value |
|---|---|
| filedes | A file descriptor that you obtained by opening the device. |
| dcmd | DCMD_I2C_REGACC |
| dev_data_ptr | A pointer to a i2c_regacc_t that's followed by additional data |
| n_bytes | sizeof(i2c_regacc_t)
+ size of additional data |
| dev_info_ptr | NULL |
The DCMD_I2C_REGACC command enables client applications to access I2C slave device registers atomically. The atomic property of this command guarantees that another client application won't interrupt the transaction by accessing the I2C bus. This command blocks until the transaction is complete.
- Input
- i2c_regops_t —
Register operations(clear, set, toggle) structure:
typedef struct { uint8_t clr; /* 1: clear; 0: no changes */ uint8_t set; /* 1: set; 0: no changes */ uint8_t toggle; /* 1: toggle; 0: no changes */ } i2c_regops_t; - i2c_regacc_t —
Register access structure:
typedef struct { i2c_addr_t slave; /* slave address */ uint32_t addr; /* register address, sent out in LSB order */ uint32_t addrlen; /* address length in byte count */ uint32_t nregs; /* number of registers to read; also length of receive data in bytes. nregs must be >= 1 */ uint32_t nregops; /* number of register operations. nregops must be either 0 or equal to nregs */ uint32_t flags; #define REGACC_RD_STOP (1 << 0) /* set stop when reading register value complete */ #define REGACC_RESEND (1 << 1) /* need to resend the send commands before register writing */ /* followed by nregs recv buffer and then nregops regop structs and then send commands if needed */ } i2c_regacc_t;Use it to read nregs of registers from addr. Then apply nregops of operations (clear, set, toggle). If necessary, write the modified value back to register.Note:- nregs must be at least 1.
- nregops must be either
0 or equal to nregs.
- When nregops == 0, RegAcc is read only.
- When nregops == nregs, RegAcc is read + modify + write.
- i2c_regops_t —
Register operations(clear, set, toggle) structure:
- Output
- i2c_regacc_t header structure
- nregs bytes of initial registers value from addr
If an error occurs, the command returns:
- EIO
- The master send failed. The causes include: bad slave address, bad bus speed, bus is busy.
- EFAULT
- An error occurred while accessing the data buffer.
- EINVAL
- Bad message format.
- ENOMEM
- Insufficient memory.
- EPERM
- The master is locked by another connection.
A code example of using DCMD_I2C_REGACC
that sends commands to the device and reads data from the registers
without applying bit modifications:
/* This sample code is accessing device /dev/i2c0. * It sends 3 commands to slave device 0x20, * then read 1 register value at offset 0x10 from * slave device 0x50 then return the value. * All the transactions are atomic. */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <errno.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <devctl.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <hw/i2c.h> #define REGS_NUM 1 #define CMDS_NUM 3 char *devname = "/dev/i2c0"; unsigned bus_speed = 0; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int i; int fd; int status; int bytes; iov_t siov[8]; iov_t riov[2]; fd = open(devname, O_RDWR); if (fd < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "open(%s): %s\n", devname, strerror(errno)); exit(-1); } if (bus_speed) { if ((status = devctl(fd, DCMD_I2C_SET_BUS_SPEED, &bus_speed, sizeof(bus_speed), NULL))) { errno = status; perror("devctl(BUS_SPEED)"); exit(-1); } } i2c_regacc_t regacc = {.slave.addr = 0x50, .slave.fmt = I2C_ADDRFMT_7BIT, .addr = 0x10, .addrlen = 1, .nregs = REGS_NUM, .nregops = 0, .flags = REGACC_RD_STOP /* Stop after read regs */ }; unsigned char recvbuf[REGS_NUM] = {0}; i2c_send_t cmds[CMDS_NUM] = {{.len = 1, .slave.addr = 0x20, .slave.fmt = I2C_ADDRFMT_7BIT, .stop = 1}, {.len = 2, .slave.addr = 0x20, .slave.fmt = I2C_ADDRFMT_7BIT, .stop = 1}, {.len = 3, .slave.addr = 0x20, .slave.fmt = I2C_ADDRFMT_7BIT, .stop = 1} }; uint8_t data0 = 0x01; uint8_t data1[2] = {0x02, 0x03}; uint8_t data2[3] = {0x04, 0x05, 0x06}; /* Header + recvbuf + regpos */ SETIOV(&siov[0], ®acc, sizeof(regacc)); SETIOV(&siov[1], &recvbuf, sizeof(recvbuf)); /* Send commands */ SETIOV(&siov[2], &cmds[0], sizeof(cmds[0])); SETIOV(&siov[3], &data0, sizeof(data0)); SETIOV(&siov[4], &cmds[1], sizeof(cmds[1])); SETIOV(&siov[5], &data1, sizeof(data1)); SETIOV(&siov[6], &cmds[2], sizeof(cmds[2])); SETIOV(&siov[7], &data2, sizeof(data2)); /* recv header + buf */ SETIOV(&riov[0], ®acc, sizeof(regacc)); SETIOV(&riov[1], &recvbuf, sizeof(recvbuf)); if ((status = devctlv(fd, DCMD_I2C_REGACC, 8, 2, siov, riov, &bytes))) { errno = status; perror("MASTER_SEND"); exit(-1); } for (i = 0; i < bytes; ++i) { fprintf(stderr, "recv: 0x%x\n", recvbuf[i]); } exit(0); }
A code example of using DCMD_I2C_REGACC
that sends commands to the device and reads data from the registers,
then applies bit modifications:
/* This sample code is accessing device /dev/i2c0. * Firstly sending 3 commands to slave device 0x20, * then read 1 register value at offset 0x10 from * slave device 0x50 and toggle the bit 2 then * write the modified value back to offset 0x10. The * original register value is returned. * All the transactions are atomic. */ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <errno.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <devctl.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <hw/i2c.h> #define REGS_NUM 1 #define OPS_NUM 1 #define CMDS_NUM 3 char *devname = "/dev/i2c0"; unsigned bus_speed = 0; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int i; int fd; int status; int bytes; iov_t siov[9]; iov_t riov[2]; fd = open(devname, O_RDWR); if (fd < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "open(%s): %s\n", devname, strerror(errno)); exit(-1); } if (bus_speed) { if ((status = devctl(fd, DCMD_I2C_SET_BUS_SPEED, &bus_speed, sizeof(bus_speed), NULL))) { errno = status; perror("devctl(BUS_SPEED)"); exit(-1); } } i2c_regacc_t regacc = {.slave.addr = 0x50, .slave.fmt = I2C_ADDRFMT_7BIT, .addr = 0x10, .addrlen = 1, .nregs = REGS_NUM, .nregops = OPS_NUM, .flags = REGACC_RD_STOP | REGACC_RESEND /* Stop after read regs and re-send cmds before write regs */ }; unsigned char recvbuf[REGS_NUM] = {0}; i2c_regops_t regops[OPS_NUM] = {{.clr = 0x00, .set = 0x00, .toggle = 0x04} /* Toggle bit 2 */ }; i2c_send_t cmds[CMDS_NUM] = {{.len = 1, .slave.addr = 0x20, .slave.fmt = I2C_ADDRFMT_7BIT, .stop = 1}, {.len = 2, .slave.addr = 0x20, .slave.fmt = I2C_ADDRFMT_7BIT, .stop = 1}, {.len = 3, .slave.addr = 0x20, .slave.fmt = I2C_ADDRFMT_7BIT, .stop = 1} }; uint8_t data0 = 0x01; uint8_t data1[2] = {0x02, 0x03}; uint8_t data2[3] = {0x04, 0x05, 0x06}; /* Header + recvbuf + regpos */ SETIOV(&siov[0], ®acc, sizeof(regacc)); SETIOV(&siov[1], &recvbuf, sizeof(recvbuf)); SETIOV(&siov[2], ®ops, sizeof(regops)); /* Send commands */ SETIOV(&siov[3], &cmds[0], sizeof(cmds[0])); SETIOV(&siov[4], &data0, sizeof(data0)); SETIOV(&siov[5], &cmds[1], sizeof(cmds[1])); SETIOV(&siov[6], &data1, sizeof(data1)); SETIOV(&siov[7], &cmds[2], sizeof(cmds[2])); SETIOV(&siov[8], &data2, sizeof(data2)); /* recv header + buf */ SETIOV(&riov[0], ®acc, sizeof(regacc)); SETIOV(&riov[1], &recvbuf, sizeof(recvbuf)); if ((status = devctlv(fd, DCMD_I2C_REGACC, 9, 2, siov, riov, &bytes))) { errno = status; perror("MASTER_SEND"); exit(-1); } for (i = 0; i < bytes; ++i) { fprintf(stderr, "recv: 0x%x\n", recvbuf[i]); } exit(0); }
Page updated: