Launching an application (without the debugger)
You can run a program without the debugger by using a command, or a launch configuration file.
Launch configurations store settings related to program execution, setup, or analysis. When you create a project, the QNX Toolkit generates a default launch configuration. But you can create your own configurations when you need to customize how a project runs and reuse those custom settings. For more information about launch configurations, go to Debugging.
The QNX Toolkit provides the launch.json in the .vscode folder to help you create launch configurations. When viewing the file, you can use the Add Configuration button to add template configurations for common tasks.
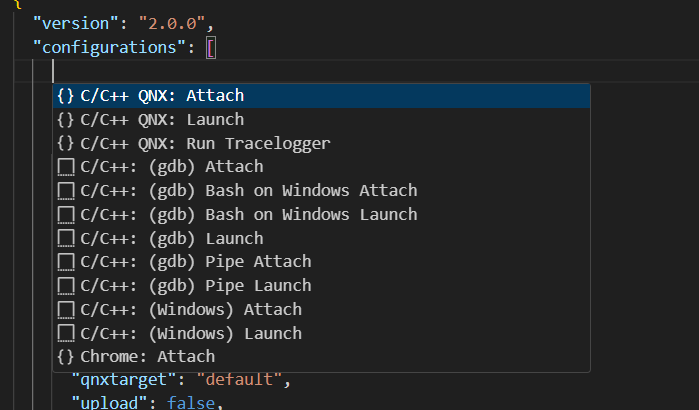
The following configurations are included:
- C/C++ QNX: Attach
- C/C++ QNX: Launch
- C/C++ QNX: Run Tracelogger
Running a program using a command
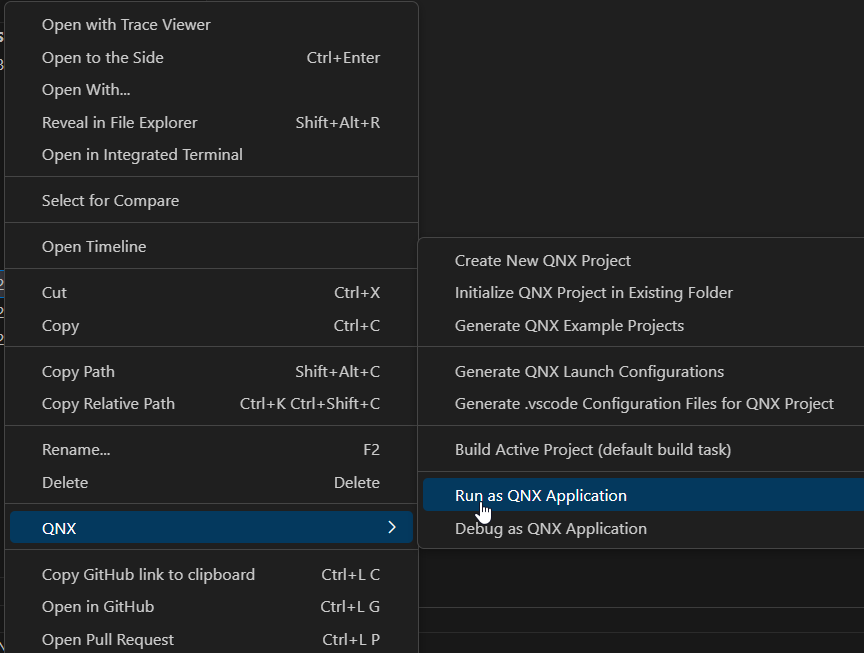
You can run a program using a QNX command.
To run the program:
- From the Workspace, right-click the program's project folder.
- Navigate to QNX > Run as QNX Application.
- Click Run as QNX Application.
- Select the default launch configuration from the palette. The QNX Toolkit uses the default settings to build and launch the program.
Running a program using the launch configuration
You can edit the launch.json file to customize the launch configuration, or create multiple launch configurations.
Creating the launch configuration:
To edit the file:
- From the workspace of the project, click the launch.json file.
- Use the Add Configuration button to add launch configurations using templates.
- Edit the fields based on your requirements.
The available options in the configuration are as follows:
qnx-gdb launch:
-
gdb — The absolute path to the host GNU debugger (e.g.,
ntox86_64-gdb). Default is per target architecture nto gdb. Default:gdb. -
program — Path to the program to launch on the host. If the program
only exists on the target, set path to
-(hyphen) and use theremotePathoption to set the path. Default:\${command:qnx.autodetectBinary}. -
remotePath — The path on the target to upload the program to.
Default is
uploadLocation/programBaseName. - args — Arguments for the program.
- env — Environment variables for the program. Default: [object Object].
-
cwd — Path to the current working directory of the target process.
Default:
uploadLocation. -
qnxtarget — Name of the target to launch the program on (configured
via Target Navigator) or
host:port. Default:default. -
stopAtEntry — If set to
true, the debugger stops at the entry-point of the target (ignored on attach). Default:false. - initCommands — Additional gdb commands to use when starting.
-
verbose — Produce verbose log output. Default:
false. - logFile — Absolute location of the log file.
-
upload — Upload the binary. Default:
true. -
uploadLocation — The folder on the remote host where temp files are
uploaded by default, including the main binary. Default:
/tmp. -
additionalSOLibSearchPath — The additional directories where the
debugger can find symbols (e.g.,
additionalSOLibSearchPath: /path/to/symbol/files). These directories are automatically added to solib-search-path for gdb. -
autoUploadSOLib — Automatically uploads required shared libraries
using
additionalSOLibSearchPathto search. Default:true. -
files — Additional files to upload or download (depending on value
of the
operationattribute) to the target before launching the program.
Example:
{
"type": "qnx-gdb",
"request": "launch",
"name": "nto/x86_64/o/bar",
"gdb": "gdb",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/nto/x86_64/o/bar",
"qnxtarget": "default",
"upload": true
},
{
"type": "qnx-gdb",
"request": "attach",
"name": "qnx attach mybinary",
"gdb": "gdb",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/nto/x86_64/o/moo",
"processId": "",
"verbose": true,
"logFile": "/tmp/attach.log",
"additionalSOLibSearchPath": "/home/elaskavaia/Develop/workspace-targets/mooly/build/x86_64-debug",
"qnxtarget": "default"
},
{
"type": "qnx-gdb",
"request": "launch",
"name": "foo",
"gdb": "none",
"program": "${command:qnx.autodetectBinary}",
"remotePath": "foo",
"qnxtarget": "default",
"env": {
"LD_PRELOAD": "/tmp/librcheck.so.1",
"MALLOC_HELP": 1
},
"preLaunchTask": "${defaultBuildTask}",
"files": [
{
"hostPath": "${env:QNX_TARGET}/${self:target.arch}/usr/lib/librcheck.so.1",
"remotePath": "/tmp/librcheck.so.1"
}
],
"upload": true
},
{
"type": "qnx-gdb",
"request": "launch",
"name": "python",
"gdb": "none",
"program": "python",
"upload": false,
"qnxtarget": "default",
"preLaunchTask": "",
"args": ["/tmp/script.py"],
"files": [
{
"hostPath": "${env:HOME}/script.py",
"remotePath": "/tmp/script.py"
}
]
}qnx-gdb attach:
- gdb — Path to gdb.
-
program — Path to the program to be debugged. Default:
${workspaceFolder}/${command:AskForProgramPath}. - remotePath — The path to the binary on the remote target (or name of the process).
- processId — Process ID to attach to. Leave empty to search by program name.
-
qnxtarget — Name of the QNX target configured using the Target
Navigator or by specifying
host:port. Default:default. -
verbose — Produce verbose log output. Default:
false. - logFile — Absolute location of the log file.
-
additionalSOLibSearchPath — The additional directories where the
debugger can find symbols (e.g.,
"additionalSOLibSearchPath": "/path/to/symbol/files"). These directories are automatically added to the solib-search-path for gdb. - initCommands — Additional gdb commands used during startup.
Example:
{
"type": "qnx-gdb",
"request": "attach",
"name": "qnx attach",
"gdb": "gdb",
"program": "${command:qnx.autodetectBinary}",
"remotePath": "${workspaceFolderBasename}",
"qnxtarget": "default"
}Using the task configuration
You can use the task configuration to modify your build commands. In the following
example, the "type":"qnx" entry indicates that the task is a
shell command (specified by "command") that has the QNX variables
sourced from qnxsdp-env.sh/bat.
Example:
{
"type": "qnx",
"label": "QNX: build debug",
"command": "make DEBUG=-g OPTIMIZE_TYPE=NONE",
"problemMatcher": [
"$gcc"
],
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
}
}Scripted file transfer
You can use a script to transfer a file or set of files to a selected target. You can specify the locations and permissions of the destination files.
Example for rsync:
rsync --perms --chmod=u+rwx,g+rwx,o+rwx /path/to/file target:/path/to/file