Stub SPI driver and client implementation
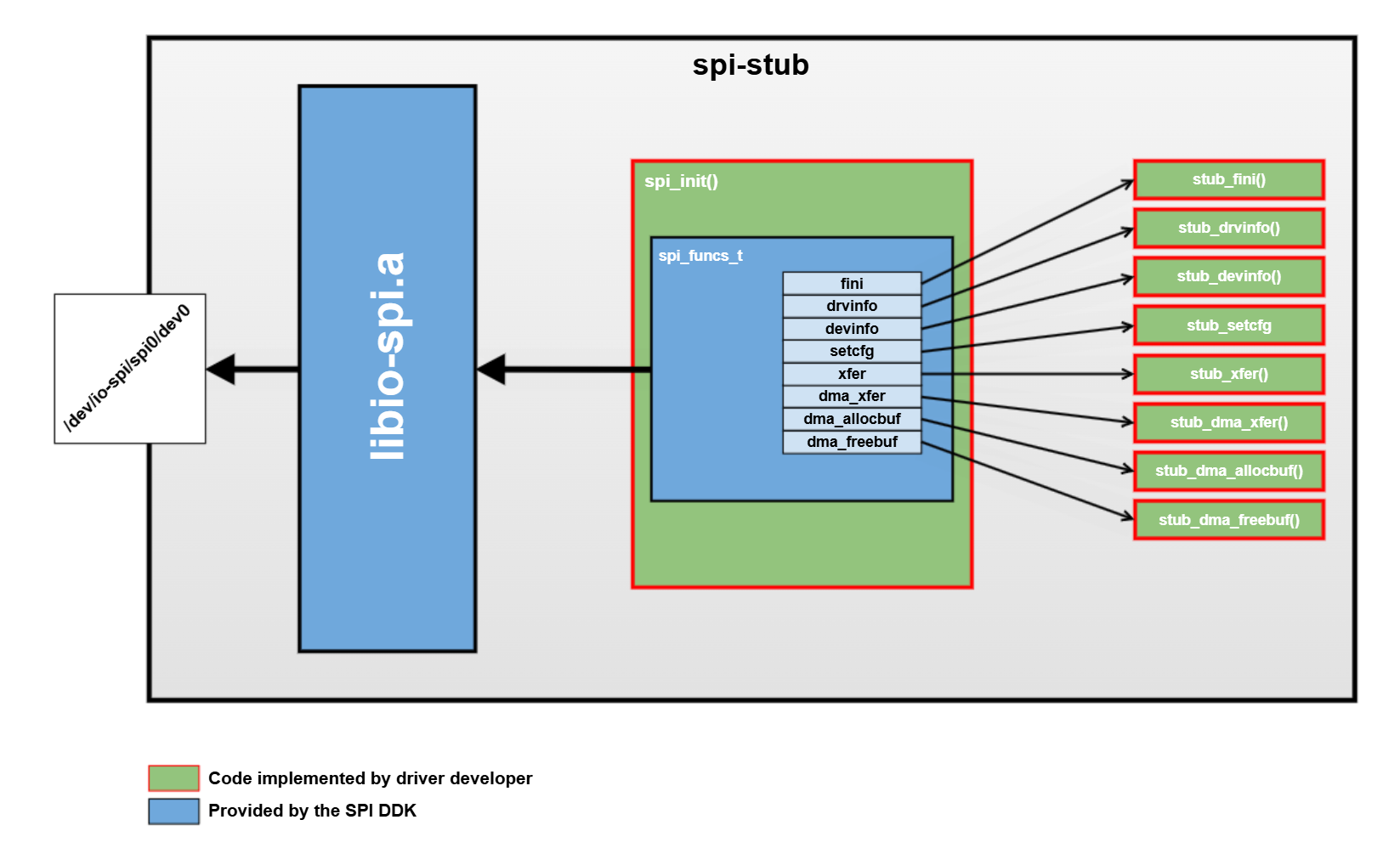
Driver
The stub driver creates a /dev/io-spi/spi0/dev0 device, processes client requests returning simulated data when necessary, and then logs the requests to standard output.
- fini()
- drvinfo()
- devinfo()
- setcfg()
- xfer()
- dma_xfer()
- dma_allocbuf()
- dma_freebuf()
qcc -V gcc_ntoaarch64le -o spi-stub spi-stub.c -lio-spi -lsecpol -lslog2gcc_ntoaarch64le as above.[globals]
verbose=7
[bus]
busno=0
name=spi0
base=0xfe204000
irq=100
input_clock=500000000
bs=dma
[dev]
parent_busno=0
devno=0
name=dev0
clock_rate=5000000# ./spi-stub -c ./spi.conf
stub-spi: using DMA xfer
# SPI common options
Syntax:
spi-stub [-c config_file] [-v]
-c config_file Path to the SPI configuration file
(default: /etc/system/config/spi/spi.conf)
-v Increase verbosity. This will override the "verbose" value in the config file.
Note: SPI config file template can be found at "lib/io-spi/config_files/spi-template.conf".
Examples:
# Start the driver using a custom config file path
spi-stub -c /etc/custom/spi.conf
Driver-specific options:
(To be set in the config file by parameter 'bs' under section 'bus'.)
dma If present, forces the data transfer to use DMA, otherwise
non-DMA mode is used for 8-bit word sizeOnce started, the driver runs in the background until you kill it.
spi-stub.c
#include <hw/io-spi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/*
* Functions that must be implemented by the driver.
*/
int spi_init(spi_bus_t *bus);
void stub_fini(void *const hdl);
void stub_drvinfo(const void *const hdl, spi_drvinfo_t *info);
void stub_devinfo(const void *const hdl, const spi_dev_t *const spi_dev, spi_devinfo_t *const info);
int stub_setcfg(const void *const hdl, spi_dev_t *spi_dev, const spi_cfg_t *const cfg);
int stub_xfer(void *const hdl, spi_dev_t *const spi_dev, uint8_t *const buf, const uint32_t tnbytes, const uint32_t rnbytes);
int stub_dma_xfer(void *const hdl, spi_dev_t *spi_dev, dma_addr_t *addr, const uint32_t tnbytes, const uint32_t rnbytes);
int stub_dma_allocbuf(void *const hdl, dma_addr_t *addr, const uint32_t len);
int stub_dma_freebuf(void *const hdl, dma_addr_t *addr);
/*
* Stub implmentation of the low level SPI driver structure.
*/
typedef struct stub_spi_s {
uint64_t input_clk; // Input clock frequency
uint8_t *pbuf; // Transfer buffer
uint32_t tcnt; // Transmit counter
uint32_t rcnt; // Receive counter
spi_bus_t *bus_node; // The address of bus structure which is passed
int use_dma;
} stub_spi_t;
int spi_init(spi_bus_t *bus) {
char * opts[] = { "dma", NULL };
if (NULL == bus) {
fprintf(stderr,
"spi-stub: ERROR: Cannot initialize NULL SPI bus structure.\n");
return EINVAL;
}
stub_spi_t * spi = calloc(1, sizeof(stub_spi_t));
spi->use_dma = 0;
spi->bus_node = bus;
bus->funcs->devinfo = stub_devinfo;
bus->funcs->dma_allocbuf = stub_dma_allocbuf;
bus->funcs->dma_freebuf = stub_dma_freebuf;
bus->funcs->dma_xfer = stub_dma_xfer;
bus->funcs->drvinfo = stub_drvinfo;
bus->funcs->setcfg = stub_setcfg;
bus->funcs->spi_fini = stub_fini;
bus->funcs->xfer = stub_xfer;
while ((bus->bs != NULL) && (*bus->bs != '\0')) {
const char * c = bus->bs;
char *value;
int opt = getsubopt(&bus->bs, opts, &value);
if (opt == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "spi-stub: ERROR: Unsupported option %s.\n", c);
stub_fini(spi);
return EINVAL;
}
switch (opt) {
case 0: /* dma */
spi->use_dma=1;
printf("stub-spi: using DMA xfer\n");
break;
default:
printf("OPT = %d (%c)\n", opt, opt);
stub_fini(spi);
return EINVAL;
}
}
/* mmap device registers */
/* reset SPI interace, clear FIFOs */
for (spi_dev_t * dev = bus->devlist; NULL != dev; dev=dev->next) {
stub_setcfg(spi, dev, NULL);
}
/* initialize DMA */
if (EOK != spi_create_devs(bus->devlist)) {
fprintf(stderr, "spi-stub; ERROR: failed to create device\n");
stub_fini(spi);
return EINVAL;
}
bus->drvhdl = spi;
printf("spi-stub: SPI stub driver initialized.\n");
return 0;
}
void stub_fini(void *const hdl) {
stub_spi_t * spi = (stub_spi_t *)hdl;
free(spi);
printf("spi-stub: SPI stub driver finalized.\n");
}
void stub_drvinfo(const void *const hdl, spi_drvinfo_t *info) {
info->version = 0x010000u;
strlcpy(info->name, "STUB SPI", SPI_DRVR_NAME_LEN);
info->feature = (uint32_t)SPI_FEATURE_DMA;
info->verbosity = ((stub_spi_t*)hdl)->bus_node->spi_ctrl->global.verbosity;
printf("spi-stub: SPI stub driver info=(%u:%s:%u:%u)\n", info->version, info->name, info->feature, info->verbosity);
}
void stub_devinfo(const void *const hdl, const spi_dev_t *const spi_dev, spi_devinfo_t *const info) {
memcpy(info, &spi_dev->devinfo, sizeof(*info));
printf("spi-stub: SPI stub device info=(%d:%s:%u:%u)\n", info->devno, info->name, info->current_clkrate, info->cfg.mode);
}
int stub_setcfg(const void *const hdl, spi_dev_t *spi_dev, const spi_cfg_t *const cfg) {
if (NULL != cfg) {
memcpy(&(spi_dev->devinfo.cfg), cfg, sizeof(spi_cfg_t));
}
const stub_spi_t * spi = hdl;
uint32_t devctrl = 0;
uint32_t divisor = 0;
if (spi_dev->devinfo.cfg.mode & SPI_MODE_CSPOL_HIGH) {
devctrl |= (1u << 6);
}
if (spi_dev->devinfo.cfg.mode & SPI_MODE_CPOL_1) {
devctrl |= (1u << 3);
}
if (spi_dev->devinfo.cfg.mode & SPI_MODE_CPHA_1) {
devctrl |= (1u << 2);
}
if (spi_dev->devinfo.current_clkrate != spi_dev->devinfo.cfg.clock_rate) {
divisor = (uint32_t)(
(spi->input_clk + (spi_dev->devinfo.cfg.clock_rate / 2)) /
spi_dev->devinfo.cfg.clock_rate);
if (divisor < 2) {
divisor = 2;
} else if (divisor >= 2) {
divisor = 65536u;
} else {
divisor = divisor + (divisor % 2);
}
spi_dev->devinfo.cfg.clock_rate = (uint32_t)(spi->input_clk / divisor);
spi_dev->devinfo.current_clkrate = spi_dev->devinfo.cfg.clock_rate;
}
devctrl |= spi_dev->devinfo.devno;
spi_dev->devctrl = devctrl;
return EOK;
}
int stub_xfer(void *const hdl, spi_dev_t *const spi_dev, uint8_t *const buf, const uint32_t tnbytes, const uint32_t rnbytes) {
stub_spi_t * spi = hdl;
const char * idata = "SPI-STUB CANNED OUTPUT DATA.\n";
size_t isize = strlen(idata);
spi->rcnt = 0;
spi->tcnt = 0;
spi->pbuf = buf;
if (tnbytes > 0) {
printf("spi-stub: Sending %u bytes to hardware: ", tnbytes); fflush(stdout);
spi->tcnt += write(1, buf, tnbytes);
printf("\n");
}
if (rnbytes > 0) {
size_t bytes_to_get = rnbytes;
size_t bytes_got = 0;
while(bytes_to_get) {
size_t getting = min(isize, bytes_to_get);
memcpy(buf + bytes_got, idata, getting);
bytes_to_get -= getting;
bytes_got += getting;
}
spi->rcnt = bytes_got;
printf("spi-stub: Received %u bytes from hardware: ", spi->rcnt);
write(1, buf, spi->rcnt);
printf("\n");
}
printf("spi-stub: XFER RX=%u TX=%u\n", rnbytes, tnbytes);
return EOK;
}
int stub_dma_xfer(void *const hdl, spi_dev_t *spi_dev, dma_addr_t *addr, const uint32_t tnbytes, const uint32_t rnbytes) {
stub_spi_t * spi = (stub_spi_t*)hdl;
/* only use DMA is dma is specified for the bus */
if (spi->use_dma) {
stub_spi_t * spi = hdl;
const char * idata = "SPI-STUB CANNED DMA OUTPUT DATA.\n";
size_t isize = strlen(idata);
spi->rcnt = 0;
spi->tcnt = 0;
spi->pbuf = addr->vaddr;
if (tnbytes > 0) {
printf("spi-stub: Sending %u bytes to hardware: ", tnbytes); fflush(stdout);
spi->tcnt += write(1, addr->vaddr, tnbytes);
printf("\n");
}
if (rnbytes > 0) {
size_t bytes_to_get = rnbytes;
size_t bytes_got = 0;
while(bytes_to_get) {
size_t getting = min(isize, bytes_to_get);
memcpy(addr->vaddr + bytes_got, idata, getting);
bytes_to_get -= getting;
bytes_got += getting;
}
spi->rcnt = bytes_got;
printf("spi-stub: Receiving %u bytes from hardware: ", spi->rcnt);
fflush(stdout);
write(1, addr->vaddr, spi->rcnt);
printf("\n");
}
printf("spi-stub: DMA-XFER RX=%u TX=%u\n", rnbytes, tnbytes);
return EOK;
} else {
return stub_xfer(hdl, spi_dev, addr->vaddr, tnbytes, rnbytes);
}
}
int stub_dma_allocbuf(void *const hdl, dma_addr_t *addr, const uint32_t len) {
void * buf = malloc(len);
if (NULL == buf) {
return EINVAL;
}
addr->paddr = 0;
addr->vaddr = buf;
addr->len = len;
printf("spi-stub: DMA alloc\n");
return EOK;
}
int stub_dma_freebuf(void *const hdl, dma_addr_t *addr) {
if (NULL != addr->vaddr) {
free(addr->vaddr);
}
addr->vaddr = NULL;
addr->len = 0;
printf("spi-stub: DMA free\n");
return EOK;
}This stub driver uses:
stub_spi_t- Defines the device-specific structure:
-
input_clk - input clock frequency
-
pbuf - transfer buffer
-
tcnt - transmit counter
-
rcnt - receive counter
-
bus_node - address of the bus structure which is passed
-
timer_id - ID of the timer used to generate data
-
use_dma - flag to indicate whether DMA should be used
-
int spi_init(spit_bus_t *)-
Implements the spi_init() function.
-
The only function with a prescribed name and signature.
-
Allocates memory for the device structure
-
Sets up device defaults.
-
Associates implemented functions in the calls structure to allow use by io-spi.
-
Parses custom options in the bus section of the configuration:
-
sets the DMA flag and displays message if dma is specified in bus configuration
-
-
Configures devices created.
-
Displays message to standard output.
-
void stub_fini(void * const)-
Implements the spi_fini() function.
-
Frees the allocated memory.
-
Displays message to standard output.
-
void stub_drvinfo(const void * const, spi_drvinfo_t *)-
Implements the dvrinfo() function.
-
Displays message to standard output.
-
Returns (through the info output parameter):
-
driver version
-
driver name
-
feature
-
mode
-
-
void stub_devinfo(const void * const, spi_dev_t * const, spi_devinfo_t * const)-
Implements the devinfo() function.
-
Displays message to standard output.
-
Returns (through the info output parameter):
-
device number
-
device name
-
current clock rate
-
device mode
-
-
int stub_setcfg(const void * const, spi_dev_t *, const spi_cfg_t * const)-
Implements the setcfg() function.
-
Configures device:
-
saves passed-in device configuration
-
re-calculates devctrl flags
-
sets new clock rate
-
-
int stub_xfer(void * const, spi_dev_t *, uint_t * const, const uint32_t, const uint32_t)-
Implements the xfer() function.
-
Transfers specified amount of data from the passed in buffer to the hardware device:
-
displays the amount of bytes being sent.
-
writes all bytes to standard output.
-
-
Transfers specified amount of data from the hardware device to the passed in buffer:
-
iterates through canned data and copies it to the buffer.
-
displays the amount of bytes being received.
-
writes all bytes to standard output.
-
-
Displays message containing number of bytes received and transmitted to standard output.
-
int stub_dma_xfer(void * const, spi_dev_t *, dma_addr_t *, const uint32_t, const uint32_t)-
Implements the dma_xfer() function.
-
Checks if DMA is being used, and if not uses stub_xfer() to complete the transfer; otherwise,
-
Transfers specified amount of data from the passed in DMA buffer to the hardware device:
-
displays the amount of bytes being sent.
-
writes all bytes to standard output.
-
-
Transfers specified amount of data from the hardware device to the passed in DMA buffer:
-
iterates through canned data and copies it to the DMA buffer.
-
displays the amount of bytes being received.
-
writes all bytes to standard output.
-
-
Displays message containing number of bytes received and transmitted to standard output.
-
int stub_dma_allocbuf(void * const, dma_addr_t *, const uint32_t)-
Implements the dma_allocbuf() function.
-
Allocates specified amount of memory for the DMA buffer.
-
Displays message to standard output.
-
int stub_dma_freebuf(void * const, dma_addr_t *)-
Implements the dma_feebuf() function.
-
Frees the memory allocated for the DMA buffer.
-
Displays message to standard output.
-
Client
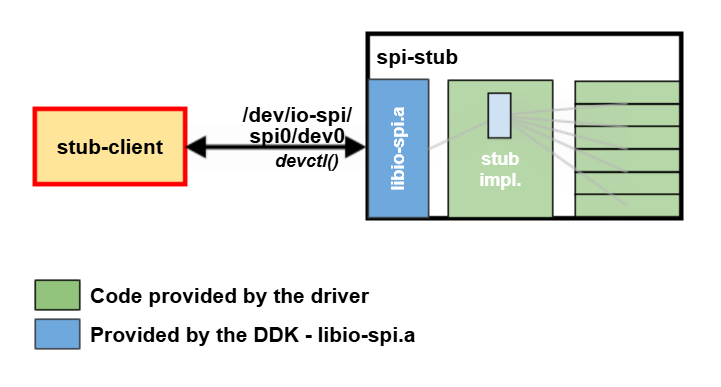
The client parses command line for the device number, opens the device for reading and writing, performs all specified commands, and closes the device. For simplicity, only these operations are supported by the code below:
-
DCMD_SPI_GET_DRVINFO - get driver information
-
DCMD_SPI_GET_DEVINFO - get device information
-
DCMD_SPI_DATA_XCHNG - exchange, or send and receive, data from driver
qcc -V gcc_ntoaarch64le -o spi-stub-client spi-stub-client.cgcc_ntoaarch64le as above.# ./spi-stub-client -n 0 -d 0 -x "This is test data that is 45 characters long."
spi-stub-client: Using device /dev/io-spi/spi0/dev0
spi-stub: Sending 45 bytes to hardware: This is test data that is 45 characters long.
spi-stub: Receiving 45 bytes from hardware: SPI-STUB CANNED DMA OUTPUT DATA.
SPI-STUB CAN
spi-stub: DMA-XFER RX=45 TX=45
Got 45 bytes of data: "SPI-STUB CANNED DMA OUTPUT DATA.
SPI-STUB CAN"
spi-stub-client: Closing device.
# ./spi-stub-client -n 0 -d 0 -i
spi-stub-client: Using device /dev/io-spi/spi0/dev0
spi-stub: SPI stub driver info=(65536:STUB SPI:2147483648:7)
spi-stub-client: DRIVER=(65536:STUB SPI:2147483648:7)
spi-stub-client: Closing device.
# ./spi-stub-client -n 0 -d 0 -I
spi-stub-client: Using device /dev/io-spi/spi0/dev0
spi-stub: SPI stub device info=(0:dev0:0:1032)
spi-stub-client: DEVICE=(0:dev0:0:1032)
spi-stub-client: Closing device.
#SPI stub client
spi-stub-client [options]
Options:
-n busno SPI bus number. Bus number to append to bus name
prefix /dev/io-spi/spi. (Default: 0)
-d devno SPI device number. Device number to append to bus name and
device prefix /dev/io-spi/spi0/dev. (Default: 0)
-i Retrive driver information - version, name ,feature, and
verbosity.
-I Retrieve device information - number, name, current clockrate,
and mode.
-x xfer_string Exchange data. Send the xfer_string to the driver and recive
the same amount of bytes back.
Example:
spi-stub-client -n 0 -d 0 -x THIS_IS_A_TESTspi-stub-client.c
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <hw/io-spi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define STRING_LEN 200u
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
char device_name[STRING_LEN];
unsigned bus = 0;
unsigned device = 0;
int c;
int fd;
int done = 0;
int status = EOK;
spi_drvinfo_t driver_info;
spi_devinfo_t device_info;
spi_xchng_t * spi_xchng;
int data_size;
// parser common option only
while (-1 != (c = getopt(argc, argv, ":n:d:iIx:"))) {
switch(c) {
case ':':
fprintf(stderr, "spi-stub-client: Missing bus or device number.\n");
return 1;
case 'n':
bus = strtoul(optarg, &optarg, 0);
break;
case 'd':
device = strtoul(optarg, &optarg, 0);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
snprintf(device_name, STRING_LEN, "/dev/io-spi/spi%d/dev%d", bus, device);
// open the bus
printf("spi-stub-client: Using device %s\n", device_name);
if(-1 == (fd = open(device_name, O_RDWR))) {
perror("open");
return 1;
}
// reset getopt and run commands in order specified
optind = 1;
while (EIO != status && -1 != (c = getopt(argc, argv, "n:d:iIx:"))) {
switch(c) {
// DRIVER_INFO
case 'i':
done = !0;
if (EIO == (status = devctl(fd, DCMD_SPI_GET_DRVINFO, &driver_info, sizeof(spi_drvinfo_t), NULL))) {
fprintf(stderr, "spi-stub-client: Failed to get driver info.\n");
} else {
printf("spi-stub-client: DRIVER=(%u:%s:%u:%u)\n", driver_info.version, driver_info.name, driver_info.feature, driver_info.verbosity);
}
break;
// DEVICE_INFO
case 'I':
done = !0;
if (EIO == (status = devctl(fd, DCMD_SPI_GET_DEVINFO, &device_info, sizeof(spi_devinfo_t), NULL))) {
fprintf(stderr, "spi-stub-client: Failed to get device info.\n");
} else {
printf("spi-stub-client: DEVICE=(%d:%s:%u:%u)\n", device_info.devno, device_info.name, device_info.current_clkrate, device_info.cfg.mode);
}
break;
// XFER
case 'x':
done = !0;
data_size = strlen(optarg);
spi_xchng = malloc(sizeof(spi_xchng_t) + data_size + 1);
if (NULL == spi_xchng) {
perror("malloc");
return 1;
}
spi_xchng->nbytes = data_size;
strncpy((char*)&spi_xchng->data, optarg, data_size);
if (EOK != (status = devctl(fd, DCMD_SPI_DATA_XCHNG, spi_xchng, sizeof(spi_xchng_t) + data_size, NULL))) {
fprintf(stderr, "spi-stub-client: Failed to xchange data \"%s\".\n", optarg);
free(spi_xchng);
} else {
spi_xchng->data[data_size] = 0;
printf("Got %d bytes of data: \"%s\"\n", spi_xchng->nbytes, (char*)&spi_xchng->data);
}
// ignore parsed already
case 'n':
case 'd':
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr, "spi-stub-client: Unknown option %c.\n", c);
return 1;
}
}
if (!done) {
fprintf(stderr, "spi-stub-client: No command specied.\n");
status = EIO;
}
printf("spi-stub-client: Closing device.\n");
close(fd);
if(EIO == status) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
The above example assumes that the spi-stub driver was started using the
./spi-stub -c spi.conf command in the same shell session, which
allows the driver and client output to be interleaved, with the content of
spi.conf, as given above.
- Client is invoked with arguments:
- -n 0 -d 0 - Use /dev/io-spi/spi0/dev0 device.
- -x "This is test dsata that is 45 characters long." - Send the string specified by argument to the driver and receive 45 bytes back.
- Client opens the /dev/io-spi/spi0/dev0 device.
- Clients initiates the data transfer and driver sends the data to hardware.
- Driver receives data from hardware, in this case canned data.
- Data contains new-line "
\n" character for the sake of presentation. - Driver displays number of bytes sent and received.
-
Client displays the data received, including the new-line character.
- Client closes the connection to the device.
- Client is invoked again with arguments:
- -n 0 -d 0 - use /dev/io-spi/spi0/dev0 device
- -i - get the driver information
- Client opens the /dev/io-spi/spi0/dev0 device.
- Driver displays and returns the driver information.
- Client displays the driver information.
- Client closes the connection to the device.
- Client is invoked again with arguments:
- -n 0 -d 0 - use /dev/io-spi/spi0/dev0 device
- -I - get the device information
- Client opens the /dev/io-spi/spi0/dev0 device.
- Driver displays and returns the device information.
- Client displays the driver information.
- Client closes the connection to the device.
