Parsing descriptors on the USB stack
Like on Linux, you now need to determine the correct endpoint to perform I/O at so that you can open a pipe and submit a URB for processing. If you have one specific qualifying device, this may already be known to you. However, if this driver is more general purpose, or you wish to store or display information about any given device, you need to parse the USB stack and its appropriate descriptors. You can read more about descriptors on this USB Descriptors page.
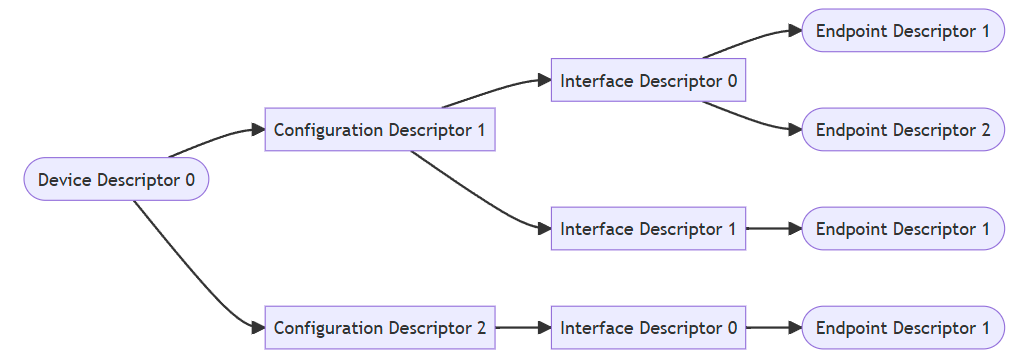
Note that in the io-usb implementation of the USB stack, Endpoint '0'
for any given interface is reserved for control, and functions as such.
Descriptors are implemented as the following data types in libusbdi:
Descriptor data types
typedef struct usbd_device_descriptor {
uint8_t bLength;
uint8_t bDescriptorType;
uint16_t bcdUSB;
uint8_t bDeviceClass;
uint8_t bDeviceSubClass;
uint8_t bDeviceProtocol;
uint8_t bMaxPacketSize0;
uint16_t idVendor;
uint16_t idProduct;
uint16_t bcdDevice;
uint8_t iManufacturer;
uint8_t iProduct;
uint8_t iSerialNumber;
uint8_t bNumConfigurations;
} usbd_device_descriptor_t;
typedef struct usbd_configuration_descriptor {
uint8_t bLength;
uint8_t bDescriptorType;
uint16_t wTotalLength;
uint8_t bNumInterfaces;
uint8_t bConfigurationValue;
uint8_t iConfiguration;
uint8_t bmAttributes;
uint8_t MaxPower;
} usbd_configuration_descriptor_t;
typedef struct usbd_interface_descriptor {
uint8_t bLength;
uint8_t bDescriptorType;
uint8_t bInterfaceNumber;
uint8_t bAlternateSetting;
uint8_t bNumEndpoints;
uint8_t bInterfaceClass;
uint8_t bInterfaceSubClass;
uint8_t bInterfaceProtocol;
uint8_t iInterface;
} usbd_interface_descriptor_t;
typedef struct usbd_endpoint_descriptor {
uint8_t bLength;
uint8_t bDescriptorType;
uint8_t bEndpointAddress;
uint8_t bmAttributes;
uint16_t wMaxPacketSize;
uint8_t bInterval;
} usbd_endpoint_descriptor_t;Methods of parsing
To parse a device, you must have an attached usbd_device_instance_t
available to parse. Once this is available, you can use the *_descriptor()
functions to parse specific levels of the tree, which are shown below:
Parsing descriptors
/* Device level descriptor */
usbd_device_descriptor_t *usbd_device_descriptor(
struct usbd_device *device,
struct usbd_desc_node **node );
/* Configuration level descriptor */
usbd_configuration_descriptor_t *usbd_configuration_descriptor(
struct usbd_device *device,
uint8_t cfg,
struct usbd_desc_node **node );
/* Interface level descriptor */
usbd_interface_descriptor_t *usbd_interface_descriptor(
struct usbd_device *device,
uint8_t cfg,
uint8_t ifc,
uint8_t alt,
struct usbd_desc_node **node );
/* Endpoint level descriptor */
usbd_endpoint_descriptor_t *usbd_endpoint_descriptor(
struct usbd_device *device,
uint8_t config,
uint8_t iface,
uint8_t alt,
uint8_t endpoint,
struct usbd_desc_node **node );The parameters represent the following:
- device
An attached device to parse.
- node
The address to a pointer where a reference to the found tree node will be stored. Can be used as a root node for searching in some functions.
- cfg
(If applicable) The configuration ID to search for or through (stored in
usbd_configuration_descriptor: bConfigurationValue).- ifc
(If applicable) The interface ID to search for or through (stored in
usbd_interface_descriptor: bInterfaceNumber).- alt
(If applicable) The interface's alternate identifier to search for or through (stored in
usbd_interface_descriptor: bAlternateSetting).- endpoint
(If applicable) The endpoint ID to search for (stored in
usbd_endpoint_descriptor: bEndpointAddress).
When parsing, note the following:
Endpoint 0 is always the control endpoint, and will have a device entry in the tree while parsing
The amount of children for any given node can be queried:
usbd_configuration_descriptor: bConfigurationValueranges from 0 tousbd_device_descriptor: bNumConfigurations- 1usbd_interface_descriptor: bInterfaceNumberranges from 0 tousbd_configuration_descriptor: bNumInterfaces- 1usbd_endpoint_descriptor: bEndpointAddressranges from 0 tousbd_interface_descriptor: bNumEndpoints- 1 (This will always be at least 1, and 0 is reserved for control)
Parsing descriptors 2
/* Generic parse */
usbd_descriptors_t *usbd_parse_descriptors(
struct usbd_device *device,
struct usbd_desc_node *root,
uint8_t type,
int index,
struct usbd_desc_node **node );When using the generic parse function, specify a type to search for and an index of which to return. Note that it returns NULL if no corresponding instance can be found.
- device
The attached device to parse.
- root
The root node to search from (gotten from another call's node).
- type
One of USB_DESC_ENDPOINT, USB_DESC_INTERFACE, USB_DESC_DEVICE, and USB_DESC_CONFIGURATION.
- index
The index of that type found.
- node
The address to a pointer where a reference to the found tree node will be stored. Can be used as a root node for searching in some functions.
Examples
Find code examples for different use-cases of parsing below.
Parsing example: direct
/* Searching for a Specific Node */
/* We can check down a specific path of the tree using the specific
* parsers as needed. For example, lets look at configuration 0, interface 1
*/
struct usbd_device *device;
// Attach Device Here - see above for info
usbd_interface_descriptor * interface_ptr;
struct usbd_desc_node *node;
/* look up interface */
interface_ptr = usbd_interface_descriptor(device, 0, 1, 0, &node);
/* Operation on node here */
if(interface_ptr == NULL){
printf("Interface Not Found\n");
}else{
/* Use desc to perform operations on the endpoint */
printf("Interface Found\n-- bLength: %d\n-- bDescriptorType: %d\n-- bInterfaceNumber: %d\n-- bAlternateSetting: %d\n-- bNumEndpoints: %d\n-- bInterfaceClass: %d\n-- bInterfaceSubClass: %d\n-- bInterfaceProtocol: %d\n-- iInterface: %d\n\n",
interface_ptr->bLength, interface_ptr->bDescriptorType, interface_ptr->bInterfaceNumber, interface_ptr->bAlternateSetting, interface_ptr->bNumEndpoints,
interface_ptr->bInterfaceClass, interface_ptr->bInterfaceSubclass, interface_ptr->bInterfaceProtocol, interface_ptr->iInterface);
}Parsing example: all of a type
/* Parsing All of a Type */
/* Assuming we have an attached device and a handle, but do not have other information, we can quickly
* parse all nodes of a type using usbd_parse_descriptors.
*/
struct usbd_device *device;
// Attach Device Here - see above for info
usbd_endpoint_descriptor_t *desc;
struct usbd_desc_node *node;
/* We pass NULL to parse the tree from the root */
for (int endpoint_index = 0; (desc = (usbd_endpoint_descriptor_t*) usbd_parse_descriptors(device, NULL, USB_DESC_ENDPOINT,
endpoint_index, &node)) != NULL, ++endpoint_index)
{
/* Use desc to perform operations on the endpoint */
printf("Endpoint @ Index %d\n-- bLength: %d\n-- bDescriptorType: %d\n-- bEndpointAddress: %d\n-- bmAttributes: %d\n-- wMaxPacketSize: %d\n-- bInterval: %d\n\n",
endpoint_index, desc->bLength, desc->bDescriptorType, desc->bEndpointAddress, desc->bmAttributes, desc->wMaxPacketSize, desc->bInterval);
}Parsing example: entire tree
/* Parsing the Entire tree */
/* Assuming we have an attached device and its handle, but no other information, we can perform a depth-first
/* search of the tree using the specific descriptors
*/
struct usbd_device *device;
//Attach device here - see above for info
usbd_device_descriptor_t *dev_desc;
struct usbd_desc_node *node;
/* Get the device's node */
dev_desc = usbd_device_descriptor(device, &node);
printf("Device %d %d\n", dev_desc->idVendor, dev_desc->idProduct);
/* Iterate through its configurations */
/* Note that configurations range from 1 to n */
for(int c = 1; c <= dev_desc->bNumConfigurations; c++){
usbd_configuration_descriptor_t *conf_desc;
conf_desc = usbd_configuration_descriptor(device, c, &node);
if(conf_desc == NULL) continue;
printf(" Configuration %d\n", conf_desc->iConfiguration);
/* Iterate though interfaces */
/* Note that interfaces range from 0 to n-1 */
for(int i = 0; i < conf_desc->bNumInterfaces; i++){
usbd_interface_descriptor_t *intf_desc;
intf_desc = usbd_interface_descriptor(device, c, i, 0, &node);
if(intf_desc == NULL) continue;
printf(" Interface %d\n", intf_desc->bInterfaceNumber);
/* Iterate through endpoints */
/* Note that endpoint 0 is control, while endpoints 1 to n are I/0. */
for(int e = 0; e <= intf_desc->bNumEndpoints; e++){
usbd_endpoint_descriptor_t *endp_desc;
endp_desc = usbd_endpoint_descriptor(device, c, i, 0, e, &node);
if(endp_desc == NULL) continue;
printf(" Endpoint %d\n", endp_desc->bEndpointAddress);
}
}
}