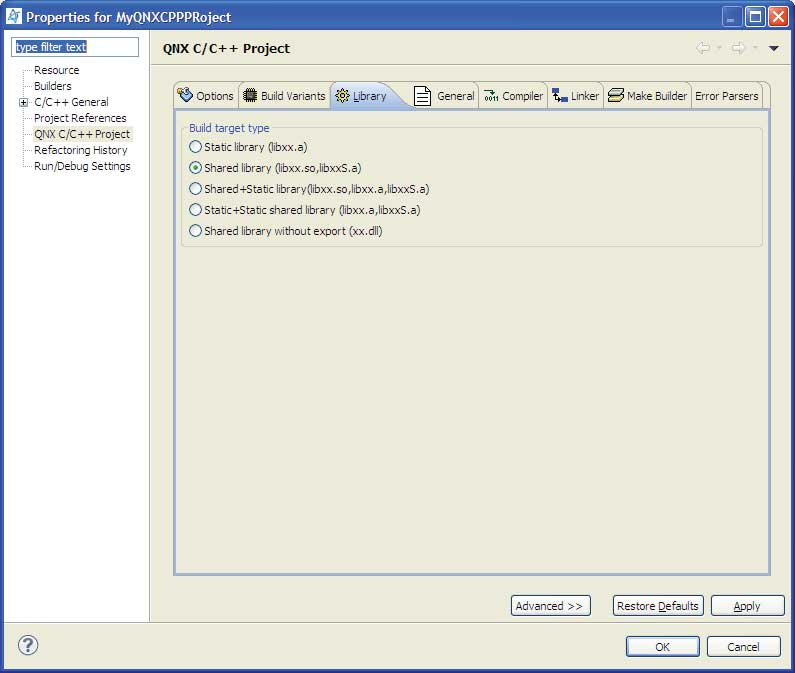
Use this tab to specify the kind of libraries that this project generates.
Note: Not all QNX projects have a Library tab; applications (executables) don't. The IDE
displays this tab only for QNX projects that build libraries.
The build target types for libraries are:
- Static library (libxx.a)
- Combines binary object (.o) files into an archive that can later be directly linked into an executable. A static library (libxx.a) is a collection of object files that you can link into an application. For this project type, the makefile is automatically created by the IDE.
- Shared library (libxx.so, libxxS.a)
- Combines binary objects and joins them so they're relocatable and can be shared by many processes. Select this option if you have code to reuse, you're interested in a relocatable library, or you want to statically link code into a shared object. When you create an application that uses a shared library, you must define your shared library's project as a Project Reference for your application.
- If you choose to use versioning (in the General Options of the Linker tab), two files are generated for a shared library: libxx.so and libxx.so.n, where n is a version number with a default of 1. The first file is a symbolic link to the latest version of the second file. If you don't use versioning, only one file (libxx.so) is generated.
- The IDE also generates a static shared library (libxxS.a). This is a collection of objects compiled to be position-independent. The static shared library lets you build custom shared libraries that use a subset of the objects from the original library, so you can remove unused functionality and thus, reduce the overhead of the library.
- Shared+Static library (libxx.so, libxx.a, libxxS.a)
- The same as selecting the Static+Static shared library (libxx.a, libxxS.a) option, except that it also builds a shared object. Selecting this option creates every kind of library that exports its symbols.
- Static+Static shared library (libxx.a, libxxS.a)
- Generates two types of libraries: A static library (libxx.a), which is meant for linking into executable programs, and a static shared library (libxxS.a), which has position-independent code (PIC) and is meant for linking into shared objects.
- Shared library without export (xx.dll)
- A shared library without versioning. The library is not linked to applications; instead, applications use it to discover extensions at runtime (e.g., driver modules that plug into hardware). Generally, you write code to open the library with the dlopen() function and to look up specific functions with the dlsym() function.