Log gamma function
Synopsis:
#include <math.h>
double gamma( double x );
double gamma_r( double x,
int* signgam);
float gammaf( float x );
float gammaf_r( float x,
int* signgam);
Arguments:
- x
- An arbitrary number.
- signgam
- (gamma_r(), gammaf_r() only) A pointer to a location where the function can store the sign of Γ(x).
Description:
The gamma() and gamma_r() functions return the natural log (ln) of the gamma() function and are equivalent to lgamma(). These functions return ln|Γ(x)|, where Γ(x) is defined as follows:
- For x > 0:
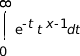
- For x < 1:
- n / (Γ( 1-x ) * sin( nx ))
The results converge when x is between 0 and 1. The Γ function has the property:
Γ(N) = Γ(N-1)×N
The gamma* functions compute the log because the Γ function grows very quickly.
The gamma() and gammaf() functions use the external integer signgam to return the sign of Γ(x), while gamma_r() and gammaf_r() use the user-allocated space addressed by signgamp.
g = signgam * exp( gamma( x ));
to compute g = Γ(x)'. Instead, compute gamma() first:
lg = gamma(x); g = signgam * exp( lg );
Note that Γ(x) must overflow when x is large enough, underflow when -x is large enough, and generate a division by 0 exception at the singularities x a nonpositive integer.
Returns:
ln|Γ(x)|
Classification:
| Safety: | |
|---|---|
| Cancellation point | No |
| Interrupt handler | No |
| Signal handler | No |
| Thread | Yes |