The source files are organized as follows:
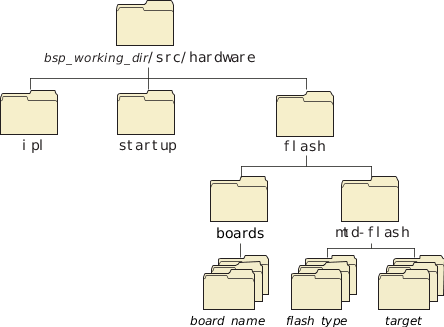 Figure 1. Flash directory structure.
Figure 1. Flash directory structure.The following pathnames apply to the flash filesystems:
| Pathname | Description |
|---|---|
| ${QNX_TARGET}/usr/include/sys | Header file f3s_mtd.h. |
| ${QNX_TARGET}/usr/include/fs | Header files f3s_api.h, f3s_socket.h, and f3s_flash.h. |
| ${QNX_TARGET}/${PROCESSOR}/lib | Libraries for flash filesystem and flash services. |
| bsp_working_dir/src/hardware/flash/boards | Source code for socket services. |
| bsp_working_dir/src/hardware/flash/mtd-flash | Source code for flash services as well as for probe routine and helper functions. |
Before you modify any source, you should:
- Create a new directory for your driver in the bsp_working_dir/src/hardware/flash/boards directory.
- Copy the files from the sample directory you want into your new directory.
For example, to create a driver called myboard based on an existing board, you would:
cd bsp_working_dir/hardware/flash/boards mkdir myboard cp -cRv existing_board myboard cd myboard make clean
The copy command (cp) specifies a recursive copy (the -R option). This will copy all files from the specified source directory including the subdirectory indicating which CPU this driver should be built for. For example, if the existing_board directory has a arm subdirectory, then the new driver (myboard in our example) will be built for ARM.