To use Mudflap in the IDE, you need to define Mudflap options to add the right flag to the compiler command for your application. There is a runtime library, libmudflap, that gets attached to the application process and is controlled by runtime options that are automatically set in the MUDFLAP_OPTIONS environment variable. This variable is set when the Mudflap tool is added to the launch configuration; the Mudflap options are also set there.
The instrumentation relies on this separate runtime library. Note that both QNX and Managed projects use the -fmudflapth option for the compiler and linker because this option supports threads (-fmudflap doesn't work with multithreaded programs).
-
Instrument the binary with Mudflap, by doing the following steps:
For a QNX project:
- In the Project Explorer, right-click a project and select Properties.
- On the left, select QNX C/C++ Project to open the properties page.
- On the Options tab, check the Build with Mudflap box.
- Click OK.
- Rebuild the project (File > Build Project).
For a Managed Project with a QNX toolchain:- In the Project Explorer, right-click a project and select Properties.
- On the left, select C/C++ Build, then Settings to open the properties page.
- On the Tool Settings tab, expand QCC Compiler, then select Output Control.
- In the configuration options on the right, check the Build with Mudflap box.
- On the Tool Settings tab, expand QCC Linker, then select Output Control.
- In the configuration options on the right, check the Build with Mudflap box.
- Click OK.
- Rebuild the project (File > Build Project).
-
To launch the instrumented binary with Mudflap enabled, do these steps:
- Open the project's launch configuration by selecting Run As > Run Configurations.
- Select the Tools tab, then click Add/Delete Tool.
-
In the Tools selection dialog, check the Mudflap box and click
OK.
The IDE displays the Mudflap tab in the launch configuration.
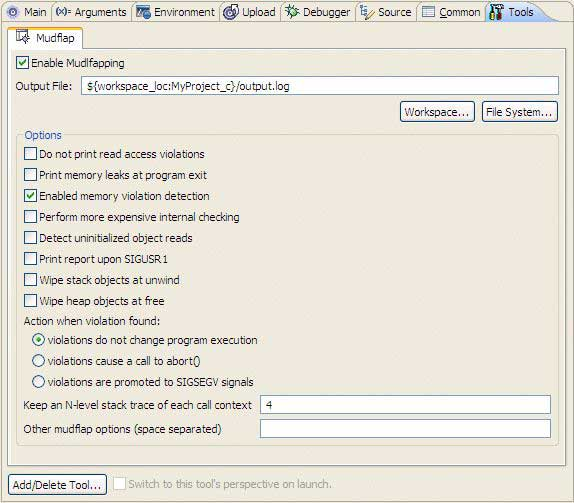
-
Configure any desired Mudflap options.
- Enable Mudflapping
- Enables the Mudflap feature to check for errors. Mudflap adds extra code to the compiled program to check for buffer overruns, which slows a program's performance (and at build time, the compiler needs to process the instrumentation code). So you should only use Mudflap during testing, and disable it in your production version.
- Output File
- Specify the location for the Mudflap output log file. Click Workspace… to specify a location in your workspace, or Filesystem… to specify a location your filesystem.
- Do not print read access violations
- Read access violations are not recorded. The Mudflap option for this feature is -ignore-reads.
- Print memory leaks at program exit
- When the program shuts down, print a list of memory objects on the heap that have not been deallocated. The Mudflap option for this feature is -print-leaks.
- Enabled memory violation protection
- Trigger a violation for every main call. This option is useful as a debugging aid. The Mudflap option for this feature is -mode-violate.
- Perform more expensive internal checking
- Periodically traverse the internal structures to assert the absence of corruption. The Mudflap option for this feature is -internal-checking.
- Detect uninitialized object reads
- Verify that the memory objects on the heap have been written to before they are read. The Mudflap option for this feature is -check-initialization.
- Print report upon SIGUSR1
- Handle signal SIGUSR1 by printing the similar report that will be printed at shutdown. This option is useful for monitoring interactions of a long running program. The Mudflap option for this feature is -sigusr1-report.
- Wipe stack objects at unwind
- Clear each tracked stack object when it goes out of scope. This options is useful as a security or debugging measure. The Mudflap option for this feature is -wipe-stack.
- Wipe heap objects at free
- Clear each tracked heap object being deallocated when it goes out of scope. This option is useful as a security or debugging measure. The Mudflap option for this feature is -wipe-heap.
- Action when violation found
- Select a specific action for Mudflap to take when it encounters a violation.
violations do not change program execution — Violations don't change the program execution. This means that this option will do nothing and the program may continue with the erroneous access; however, this action may corrupt its own state, or the state of libmudflap. The Mudflap option for this feature is -viol-nop.
violations cause a call to abort() — A call is made to the abort function when a violation is encountered, which then requests a core dump and exit. The Mudflap option for this feature is -viol-abort.
violations are promoted to SIGSEGV signals — Generate a SIGSEGV, which a program may choose to catch. The Mudflap option for this feature is -viol-segv.
- Keep an N-level stack trace of each call context
- Record N levels of tack backtrace information for each allocation, deallocation, and violation. The Mudflap option for this feature is -backtrace=N.
- Other Mudflap options (space separated)
- A field where you can specify additional Mudflap options. For information about these options, see Options for Mudflap below.
- Click Run or Debug to launch the application.