The /etc/system/sysinit script runs /etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit to do local initialization of your system.
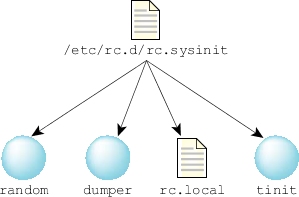 Figure 1. Initialization done by /etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit.
Figure 1. Initialization done by /etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit.The rc.sysinit script does the following:
- It starts a secure random-number generator, random, to provide random numbers for use in encryption and so on.
- If the /var/dumps directory exists, rc.sysinit starts the dumper utility to capture (in /var/dumps) dumps of processes that terminate abnormally.
- If /etc/host_cfg/$HOSTNAME/rc.d/rc.local exists and is executable, rc.sysinit runs it. Otherwise, if /etc/rc.d/rc.local exists and is executable, rc.sysinit runs it. There isn't a default version of this file; you must create it if you want to use it. For more information, see "rc.local," below.
- Finally, rc.sysinit runs tinit. By default, rc.sysinit tells tinit to use text mode. For more information, see "tinit."