The mm-stream service uses other platform services to read audio and video content.
- the libasound library, which talks to the io-audio server to obtain raw audio input
- the Screen Graphics Subsystem
- the Camera Framework
- standard POSIX file operations
Whether the content must be stored on the same node or it can be read from another node depends on the particular service used. For example, for media files visible through NFS, mm-stream can access those remote files through POSIX calls. Likewise, the Camera Framework allows its clients to read camera feeds originating from another node as long as it's mounted in the local filesystem.
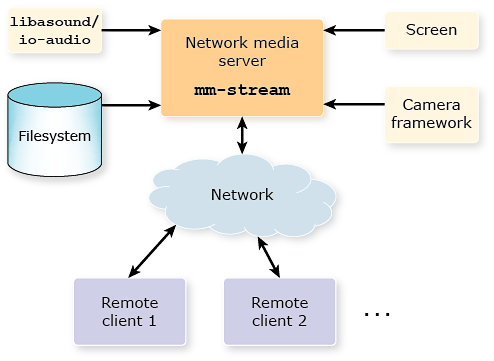
Figure 1. Integration of mm-stream with other services
Communication between the network media server and the services that provide media input is done through shared libraries. These are loaded by mm-stream and they read the inputs based on configuration parameters such as the audio sampling rate and the video dimensions and frame rate. Remote clients access the content from mm-stream through RTP and RTSP. Pure RTP is used for multicasting, when multiple media players (clients) receive a media stream with minimal bandwidth cost. RTSP is used when a media player wants to control streaming through playback commands (e.g., play, pause).