Display and manage the on-screen keyboard
Syntax:
keyboard-imf [-d device] [-U group:user]
Runs on:
QNX Neutrino
Options:
- -d
- The display required for the board (see "Display types" below).
- -U UID:GID
- The user ID and the group ID under which to run keyboard-imf.
Description:
The keyboard-imf service acts as an intermediary between keyboard-dependent applications and underlying keyboard services. For instance, the keyboard service works with the keyboard provided by the HMI to display and manage the on-screen keyboard, or with a physical keyboard to enable input from that keyboard.
- show and hide the keyboard
- know the keyboard height (in pixels) so they can, if necessary, adjust their displays to fit into the remaining available screen area
- accept text entries and know how many characters have been entered
Interaction of HMI, keyboards, and applications
The diagram below shows how keyboard-imf interacts with the HMI virtual keyboards:
- The HMI virtual keyboards (HTML inside the Navigator, or Qt standalone) create the /pps/system/keyboard/control and /pps/system/keyboard/status PPS objects, and publish their activities to them.
- The keyboard-imf service subscribes to these objects to be able to receive information from the HMI.
- The keyboard-imf service creates the /pps/services/input/control PPS object, to which it publishes information received from the HMI and the applications. This object is for internal communication between keyboard-imf and the HMI; other components and applications don't need to publish or subscribe to this object.
- Applications, such as Weblauncher and Qt runtime, subscribe to /pps/services/input/control to learn about keyboard presence, height, etc., and publish information, such as the user input and the number of characters entered.
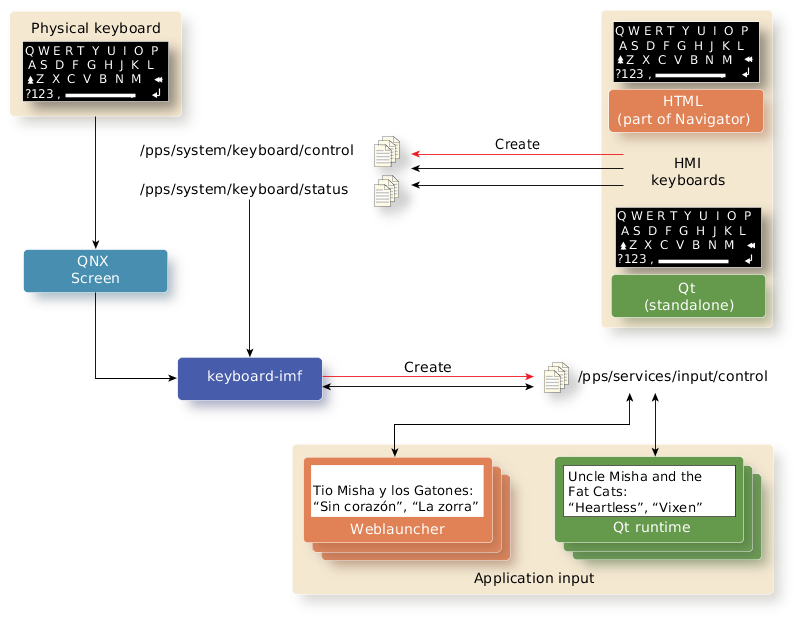 Figure 1. Keyboards, keyboard-imf and applications.
Figure 1. Keyboards, keyboard-imf and applications.Physical keyboard
- Configure the globals input parameter in the Screen configuration file (graphics.conf) to accept input from a physical keyboard. For more information, see "Configuration parameters for globals" in the Screen Graphics Subsystem Developer's Guide.
- Make sure that your system has the language-specific key-mapping files for the languages you will support. These files should be in the /usr/share/keyboard/ directory.
- Set the HAS_SOFTWARE_KEYBOARD environment variable to
true or false on the target. You can use
the variable to change your application's behavior. For example, the Browser
app resizes to move the URL bar above the software
keyboard if the environment variable is set to true.
Conversely, if the variable is set to false, the
Browser app doesn't resize.
You can set the environment variable in the /scripts/env.override.variant file.
For more information about how keyboard-imf interacts with applications and underlying keyboard services, see "Interaction of HMI, keyboards, and applications".
Display types:
The -d option must be set for your board's display. For OMAP5432 boards, set it to hdmi; for SABRE Smart Device boards, set it to internal. Possible display types are listed in the /etc/system/config/graphics.conf configuration file. When you are configuring your system, you will need to edit this file and enter the display type(s) supported on your board, as well as other graphics configuration values.
For more information about the /etc/system/config/graphics.conf configuration file and how to configure it, see the chapter "Screen Configuration" in the Screen Graphics Subsystem Developer's Guide.
PPS objects:
- /pps/services/input/control/
This object is for internal communication between keyboard-imf and the HMI; other components and applications don't need to publish or subscribe to this object.